For many people, playing games is a source of joy. Because a game is a visual medium where one can experience a completely different life than in reality.
Furthermore, the game in visual ways describes the character’s individuality, the game’s tale, the procedures for completing each level, and several other visual unique elements.
We should realize that games are not just for entertainment only, they can be a mode for learning science for students. As a result, it should come as no surprise that students may create games to solve mathematical problems.

Games can likewise be utilized as instructional media just as we are going to create an Algebra Game in Scratch, a programming language.
How to Make an Algebra Game in Scratch
One of the platforms for making games, which is famous among students and kids, is Scratch.
Kids can make games on Scratch related to numerical rationale, so that learning math-science concepts will be more obvious utilizing the game technique.
Polynomial Equation, for example, is one of the numerical conditions. And some students find it difficult to understand.
We can develop games to solve problems linked with this concept on the Scratch platform.
An example of a polynomial equation problem is
x2 − 4x + 7 (1)
What is a Polynomial Function?
A polynomial function is simply a quadratic function, a quadratic polynomial, a polynomial of degree 2, or simply a quadratic. A univariate (single-variable) quadratic function, for example, has the form
f(x) = ax2 − bx + c, a ≠ 0 (2)
If equation (1) is clarified with equation (2) then
a= 1, b= 4, c= 7
We will use a, b, and c to define coding variables on the Scratch platform, as shown in the image below.
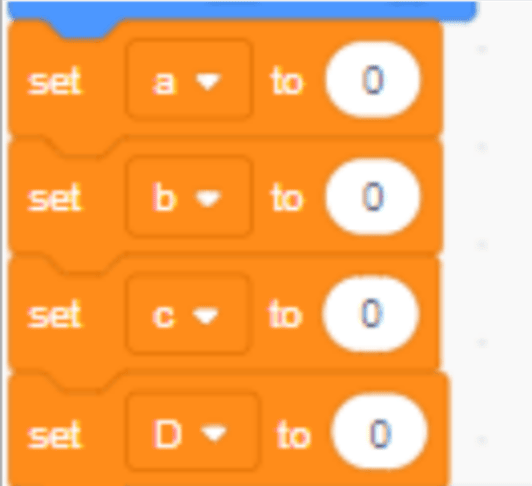
https://scratch.mit.edu/projects/646170240
In the quadratic equations, the expression underneath the square root sign is called the discriminant of the quadratic equation and is defined as a D variable or an upper case Greek delta
∆= b2 − 4ac (3)
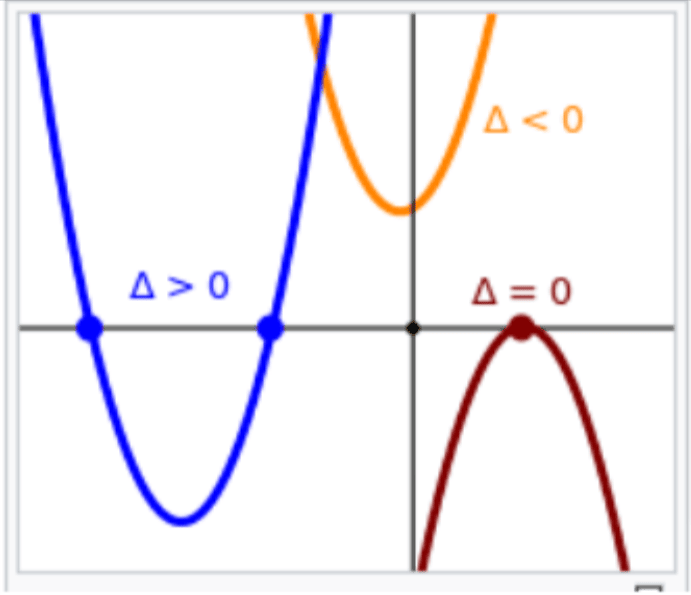
(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quadratic_equation)
Delta (∆) in Figure 1 has been defined as a D variable, then the next step is to set the coding for equation (3) in the coding area in Scratch.
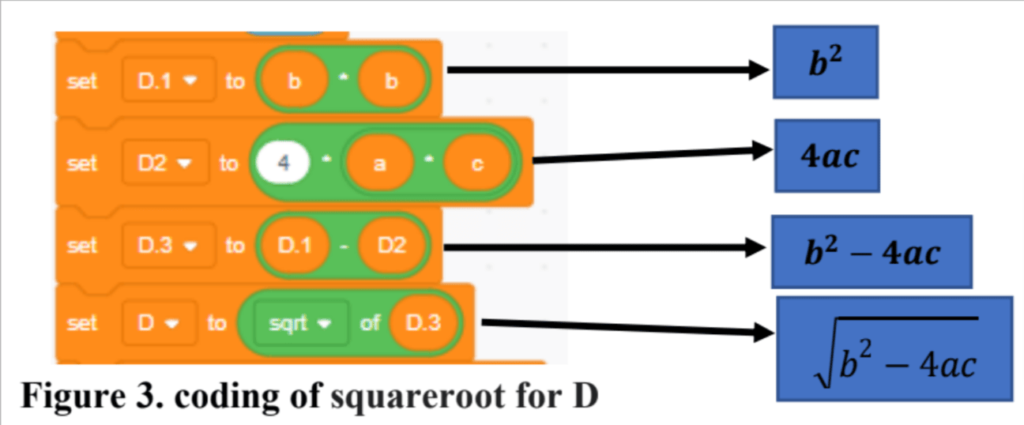
In the next stage after setting the coding for Delta, we will set the coding to determine exact roots, the formula for exact roots is (4 and 5).
r1= −b − √b2 − 4ac/2a (4)
r2= −b +√b2 − 4ac/2a (5)
We can arrange equations 4 and 5 with block coding as shown in Figure 5.
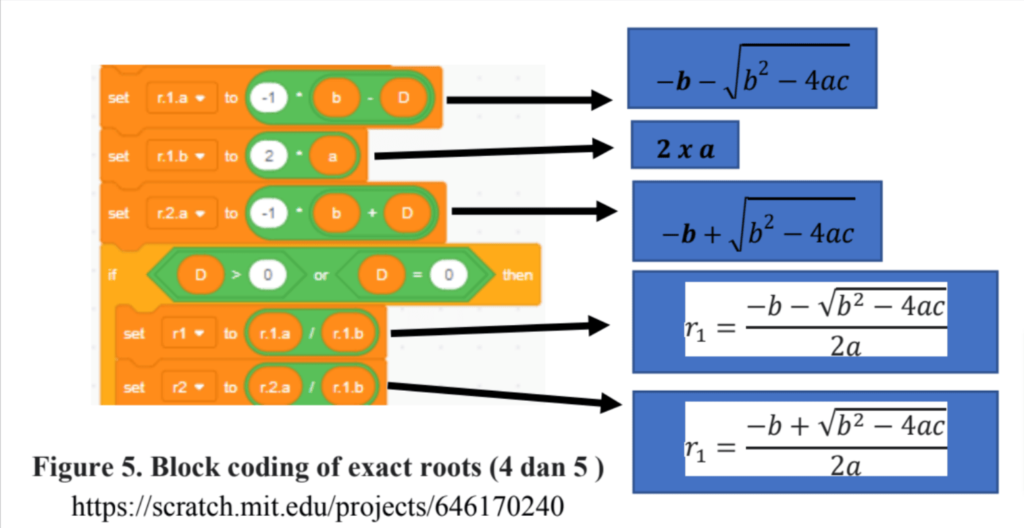
In Figures 3 and 5, there are green blocks, these blocks can be taken from the “operator” code type. The complete Game-solving mathematical Polynomial Equations in Scratch can be viewed here.
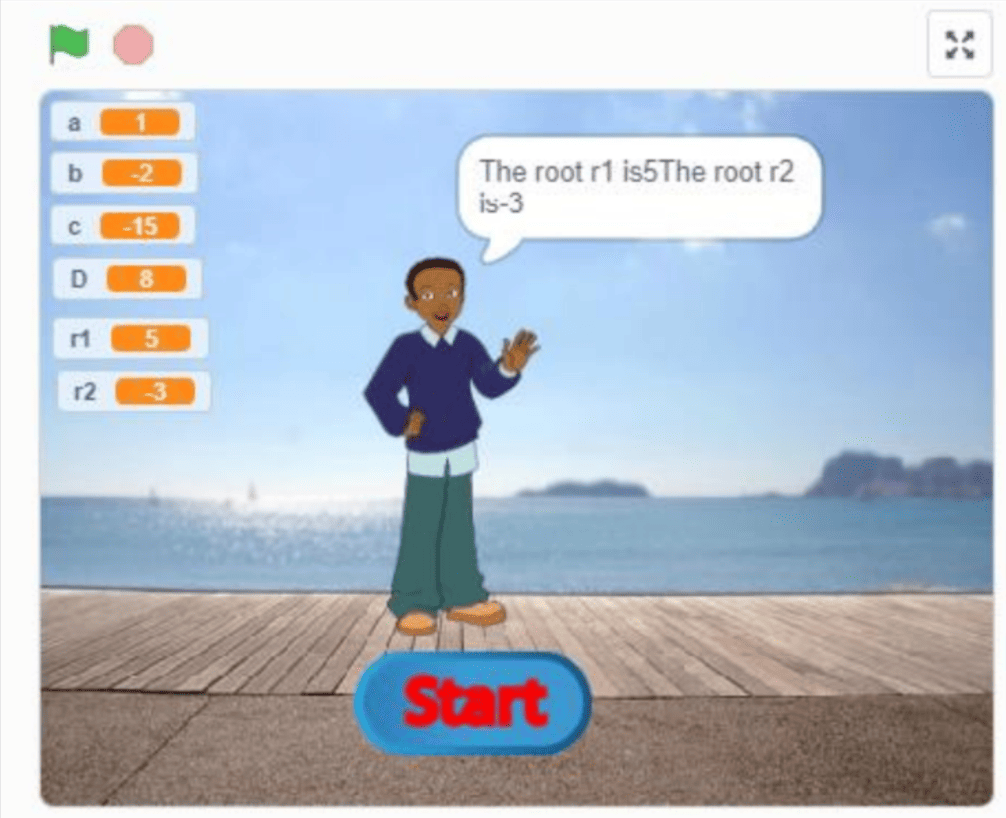
We can also test Polynomial Equations math problems that are calculated manually here.
As an example;
x2 − 2x − 15 = 0
https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/d93/db8935165a9583f953a8e894d73e153b.pdf
a= 1, b= -2, c= 15, r1= 5, r2= -3
Conclusion
Understanding mathematical concepts become easier with coding, and you can even create various mathematical games.
These games can be simple problem solvers. You can use any mathematical concept; in this case, we used polynomial equations.
If you want to make this Algebra game in Scratch, go to Scratch, follow the usual project creation procedures, and add the codes given above in the same order.
In terms of the backdrop and sprites, you can customize the game to your liking. If you add all the codes correctly, your game should be ready and look similar to the one in Figure 6.
Learn Scratch at BrightChamps with its specially designed curriculum that makes learning programming easy for students in Grade 1-12.
BrightChamps also teaches a variety of other programs that help kids build a foundation in computer programming through activities, interactive lessons, and other means.






![Ultimate List of 30 Best Scratch Games for Kids [2022 Edition]](https://pages.brightchamps.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/Ultimate-List-of-Scratch-Games-for-kids-400x250.jpg)




